CYTOPLASM:-
The cytoplasm is a semi-viscous substance or a fluid content bounded by the plasma membrane. This cytoplasm is present in both plant and animal cells. All the cellular contents in prokaryotes are present in the cytoplasm whereas in eukaryotes, the nucleus of the cell is separated from the cell's cytoplasm. The cytoplasm was first discovered by Robert Brown in the year 1835.
Previously, it was believed that essence of life was stored in the fluid present in the cell and was named as "protoplasm" which means life fluid, but later it was clear that the fluid is a basic medium where the various particles float around in it. And then later, it was understood that the life resided in a cell after the discovery of the nucleus. Hence the protoplasm was named as "Cytoplasm".
The main components of the cytoplasm are:
- Cytosol: a gel like substance
- Cell organelles: the internal sub-structures and organelles in it.
- and cytoplasmic inclusions
Cytosol:
The cytosol is the part of the cytoplasm that is not occupied by any organelle. It is a gelatinous fluids, where other components of the cytoplasm remain suspended. It is also the aqueous portion of the extracellular protoplasm and of nucleoplasm (nuclear protoplasm). It mainly consists of the cytoskeleton filaments, organic molecules, salt , water, glucose, aminoacids, minerals and ions etc
The cytosol can also be differentiated in the two ways. They are:
-a)The outer clear and peripheral layer of cytosol which is relatively non-granular viscous, clear and rigid is called as "Ectoplasm" or the "cell cortex"
-b)The inner portion of cytosol which is granular and less viscous is called as "Endoplasm"
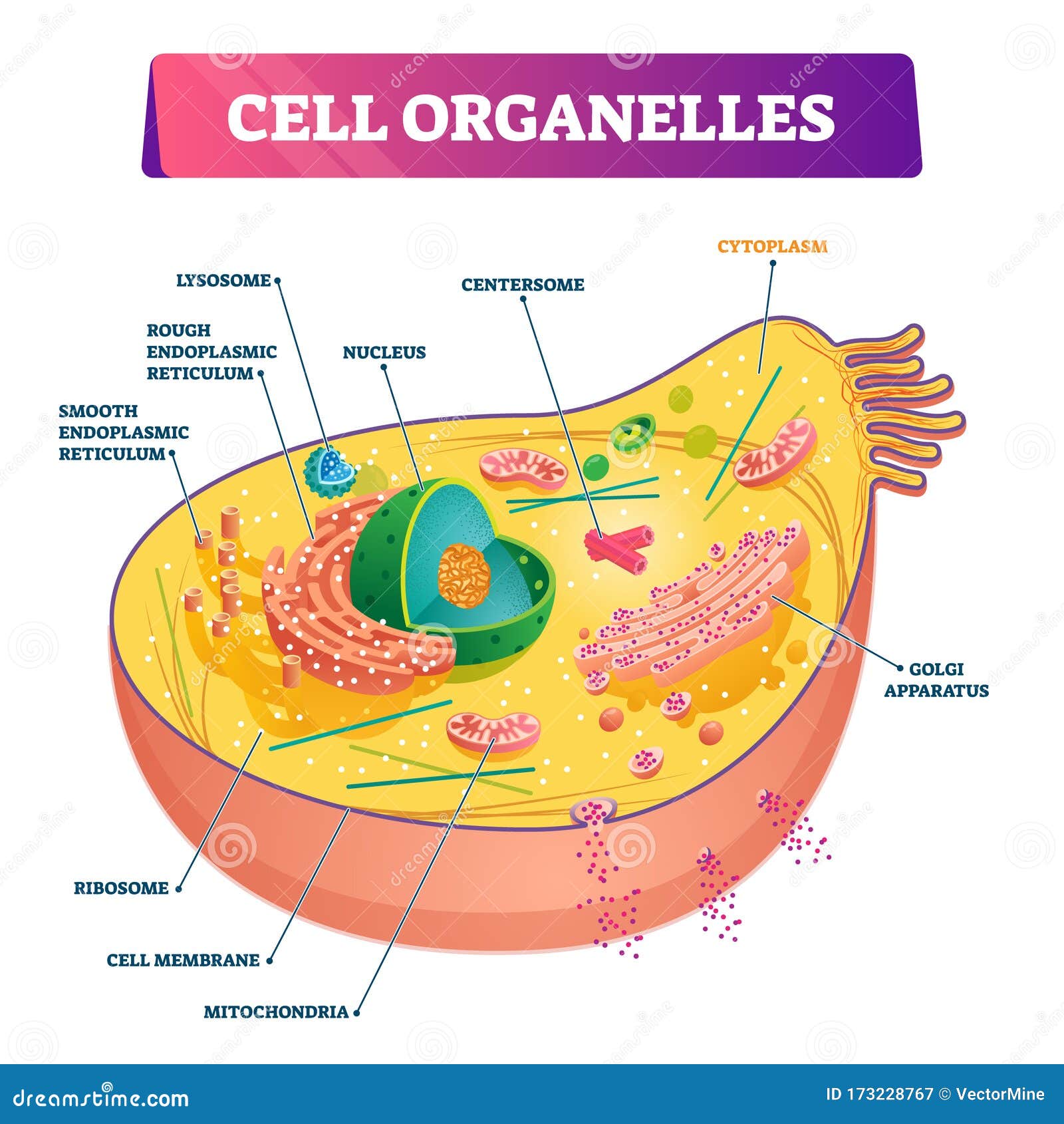
Cell organelles:
The term "organelles" means little organs, that are membrane bound. They are present in the cell and perform various functions that are necessary for the survival of the cell. These living structures remain suspended in the cytosol. Some of the cell organelles are Endoplasmic reticulum, plastids, Mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, Lysosomes, Ribosomes, Vacuoles etc. In addition to that, chloroplast is also present in the plant cells.
Cytoplasmic inclusions:
The non living structures suspended in the cytosol are referred to as Cytoplasmic inclusions. These consist of different types of insoluble molecules that remain suspended in the cytosol. All these inclusions are not surrounded by any membrane. They are basically granules of starch and glycogen that store food and energy. The cytoplasmic inclusions include oil drops, calcium oxalate crystals or silicon dioxide crystals, tri-aceyl glycerols, pro-granules, secretory granules,lipid droplets etc
Some of the properties of cytoplasm are described below:-
- The cytoplasm is made up of 70-80% water and usually colourless.
- It contains proteins, carbohydrates, salts, sugars, aminoacids, nucleotides etc.
- The cytoskeleton of the cytoplasm gives the cell its shape.
- Cytoplasm also helps the movement of the cellular materials around the cell through a process called as "cytoplasmic streaming"
- Since the cytoplasm constitutes of numerous salts, it is a very good conductor of electricity.
- It also shows different staining properties, the areas stained with basic dyes are the basophilic areas of the cytoplasm.
Functions of cytoplasm:
- The cytoplasm is the site of various enzymatic reactions and metabolic activities of the cell.
- It also maintains the cell's shape and consistency and provides the suspension medium to the cell organelles.
- The cytoplasm also acts as a buffer and protects the genetic material of the cell and also prevents the external or mechanical injury of the cell and cell organelles.
- All the types of cell functions like cell expansion, growth and replication are carried out in the cytoplasm of cell.
- The translation of mRNA into proteins on ribosomes also occurs mostly in the cytoplasm.
- Cellular respiration begins in the cytoplasm with glycolysis.
Excellent matter
ReplyDelete