MITOCHONDRIA:
Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles found in the cytoplasm of almost all eukaryotic cells. These are mainly associated with cellular respiration ie, to generate large quantities of energy in the form of Adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The word mitochondria is derived from two Greek words "mito" means "thread" and "chondrian" means "granule". Hence these are thread-like or granular cytoplasmic organelles. The structure of mitochondria was first recognized by "Albert Von Kolliker" in the year 1880 but later the term mitochondria were introduced by "Benda" in the year 1898.

These mitochondria are the organelles that convert energy into usable forms and plays a vital role in generating and transforming energy. They are double membranes, and also semi-autonomous organelles. These are found in both in plant and animal cells but they are absent in prokaryotes. They contain many enzymes and coenzymes which are responsible for energy metabolism. It is otherwise called as "Power House of the cell" as it plays the main role in cellular respiration.
Structure of mitochondria:
The shape of the mitochondria may change from one cell to another depending upon the physiological conditions of the cell. They are typically round or oval in shape and the size of the mitochondria is highly variable. It's length varies from 3-10 microns and width from 0.2-0.1 microns. There are about 2000 mitochondria per cell representing about 25% of the cell volume. The number of mitochondria per cell varies widely, for example; in humans, erythrocytes (RBCs) do not contain any mitochondria whereas liver cells and muscle cells may contain hundreds or even thousands.
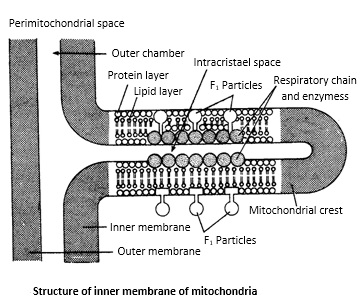
The mitochondrion is bounded by two membranes- outer membrane and inner membrane. Both the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes are 60-70A thick. The outer membrane consists of more phospholipids and cholesterol than the inner membrane. The space between the two membranes is called as "peri-mitochondrial space" which is filled with fluid.
Outer membrane:
- The outer membrane is smooth and resembles its structure with that of the plasma membrane.
- There are small structures called as 'porins' that are present in the outer membrane.
- These porins allow the exchange of molecules between the cytoplasm and inter-membrane space.
Inner membrane:
- The space-bound by inner membrane is called as "inner membrane space" or "inner chamber".
- This inner chamber is filled with a mitochondrial matrix that contains dense granules, circular mitochondrial DNA, and 70S ribosomes.
- This inner mitochondrial membrane is rich in many enzymes, coenzymes, and also other components.
- It also contains protein pumps and protease proteins for the transport of various molecules such as ATP, citrates, ADP, and phosphates.
- The inner membrane also produces a series of folds or finger-like projections called "cristae"
- The mitochondrial membrane contains small particles called as 'elementary particles' or F1 particles of electron transport particles (ETP).
- ETP of the inner membrane is stalked and each stalked particle consists of a stalk, head, and also a base.
Functions of Mitochondria:
- The main function of mitochondria is to supply all the required energy and only these are capable of converting pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water.
- These are the respiratory centres of the cell and hence the powerhouse of the cell.
- Mitochondria help to maintain the proper concentration of calcium ions within the compartments of the cell.
- Mitochondria produces heat (brown fat) and iron-containing pigments and also helps in building certain parts of blood and hormones.
- It also plays an important role in the process of apoptosis or programmed cell death.
- Mitochondria take part in cellular respiration activities such as Glycolysis, Kreb's cycle, electron transport system, Oxidative phosphorylation, Oxidative decarboxylation, and many more, etc.
- Images courtesy by google images
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeletevery useful thank you ma'am.
ReplyDelete