LYSOSOMES:
Lysosomes are membrane-bound tiny bags filled with the hydrolytic enzymes that are concerned with both intracellular and extracellular digestion. A typical lysosome is a lytic body that is capable of lysis. Lysosomes can occur freely in the cytoplasm. The word "lysosome" is made up of two words ie, 'lyso' means 'digestive' or 'breakdown', and 'soma' means 'body'. These lysosomes were first named as "pericanalicular bodies" because of their location but later it was renamed as lysosomes by"Christian de Duva" in the year 1955.
Lysosomes occur in most animal cells and in a few plant cells too, (in the form of vacuoles). They are most abundant in the cells which are related to enzymatic reactions such as liver cells, pancreatic cells, kidney cells, spleen cells, leukocytes, etc except in the RBCs.

Structure of lysosomes:
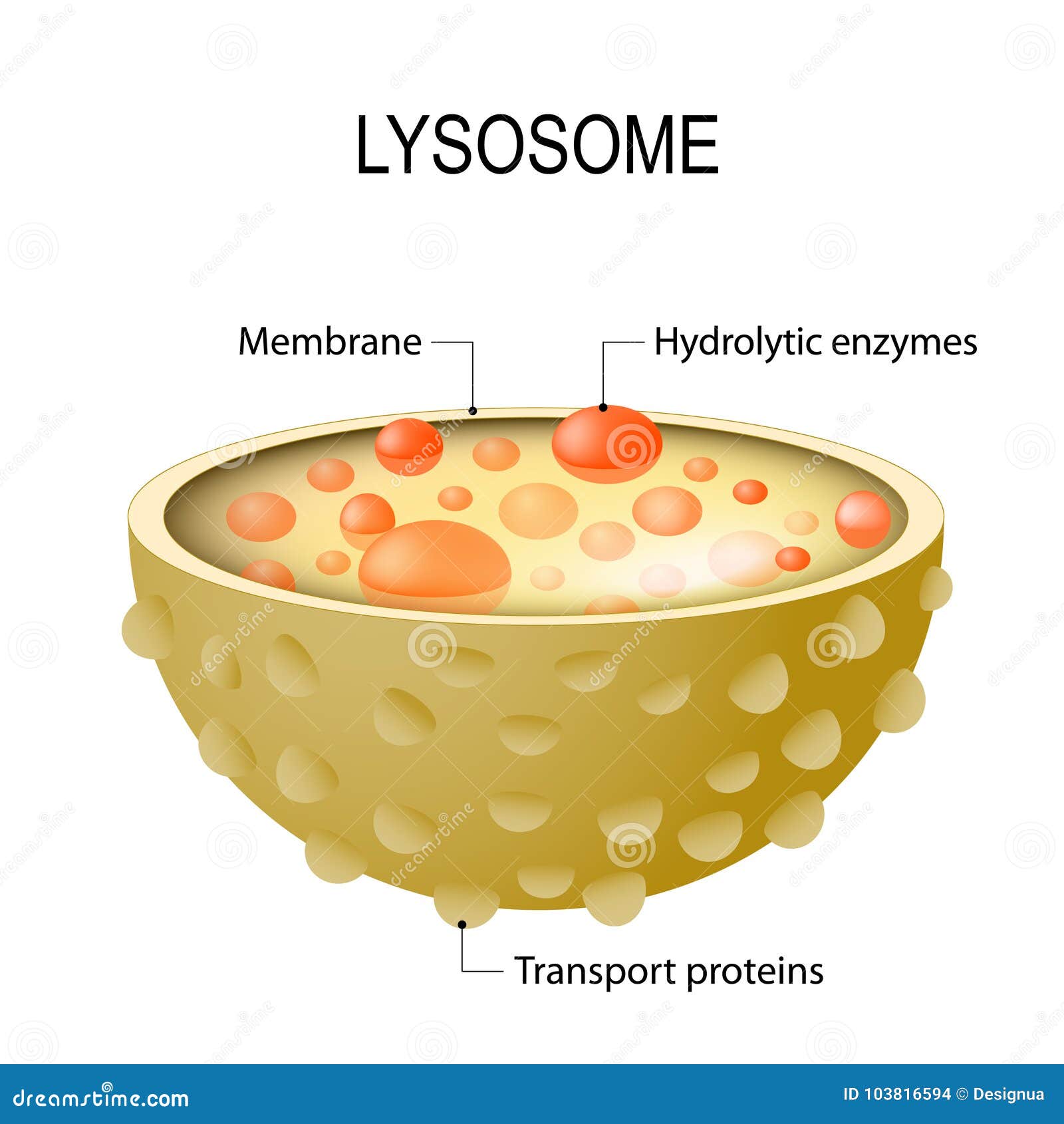
Lysosomes are spherical dense bodies filled with large granules of digestive enzymes and acid phosphatases. Lysosomes are spherical in shape, but they are irregular in certain meristematic cells of roots. The size of the lysosomes usually ranges from 0.2-0.8 in diameter but may be exceptionally large as 8 microns in mammalian kidney cells and leucocytes. The lysosomes are bounded by a single-layered membrane in contrast to the double-layered membranes of other organelles. It is made up of proteins and lipids.
The interior of some lysosomes is uniformly solid while others have a very dense outer zone and a less dense inner zone. The inner of the lysosome is acidic with a pH of 4.8, but the pH of the surrounding cytosol is 7.2. The low pH is maintained by pumping the protons from the cytosol. Lysosomes are polymorphic structures because of their contents vary in the stages of digestion.

Types of Lysosomes:
- Primary lysosomes: These are small sac-like structures enclosing enzymes synthesized by the rough endoplasmic reticulum. They are also said to be storage granules as they store enzymes. The enzymes present in primary lysosomes are acid hydrolases.
- Secondary lysosomes: These are formed by the fusion of primary lysosomes with phagosomes. They contain engulfed materials and enzymes.
- Residual lysosomes: The secondary lysosomes with the undigested wastes (residues) are called as residual lysosomes. The digested materials are diffused into the cell cytoplasm through the lysosomal membrane.
Lysosomes mainly involve in these activities:
- Intracellular digestion:- It follows in various aspects:
- Autophagy:
Autophagy refers to the lysosomal digestion of own cell components where 'auto' means 'self'' and 'phago' means 'eating'. Here the cell organelles, worn-out cells, dead cells, cell debris, and stored food materials are digested by the lysosomes. In autophagy, the organelle to be digested is enclosed by a membrane called 'isolation membrane' (derived from ER or Golgi body)
The cell to be digested enters into this membrane and forms an "isolation body". This isolation body fuses with the lysosome to form autophagic vesicles and is digested. The digested particles now diffuse into the cytoplasm and are utilized by the cell for metabolic activities.

- Heterophagy:
It is the lysosomal digestion of foreign materials. Here the cell digests the foreign or extracellular food materials. These food materials are taken into the cells by endocytosis such as phagocytosis.
- Autolysis:
Autolysis refers to the killing of entire set of cells by breakdown of the lysosomal membrane. Here auto means 'self' and lysis means 'kill'. In autolysis, the lysosome digests its own cell; hence autolysis is called as "cellular autolysis". In this process, the lysosome ruptures inside its cell, and the released enzymes digest and degrade the cell. As the lysosome kills its own cell, it is called as "suicidal bag".Hence lysosomes are known as "Suicidal bags of cell"
2. Extracellular digestion:
The digestion of materials outside the cell is called "Extracellular digestion". On certain occasions, lysosomes release enzymes outside the cell by exocytosis and bring about digestion. For eg; this digestion occurs during bone erosion. The osteoclasts are rich in lysosomes. In the area of erosion, the lysosomes release enzymes outside the cell and bring about the extracellular digestion of bone.
Other functions of lysosomes are:-
- Fertilization:- The acrosome of sperm ruptures and releases enzymes such as hyaluronidase, proteases, etc which dissolve the egg membrane and make a way for the entry of sperm into the egg.
- Chromosomal breakage:-The lysosomes contain the enzyme deoxyribonuclease. This enzyme attacks the chromosome and brings about chromosomal breakages.
- Programmed cell death is also caused by lysosomes.
- Lysosomes also help in the developmental process.
- Lysosomes function as a garage disposal system of the cell.
- Autolysis occurs during amphibian metamorphosis, insect metamorphosis, menstruation, etc
- Lysosomes bring about intracellular digestion and extracellular digestion.

- courtesy by google images
No comments:
Post a Comment